CEZO

INTRODUCTION
Conventional web applications have a frontend and a backend. The frontend is all that the clients sees when entering a site page. The entire of the HTML, CSS and JS are utilized to show the frontend and are utilized to interface with the backend. The backend is the place where all the bosses are finished for the site, for instance an educational record connection and serving the customer data about their profile. Java, Python or Node.js are utilized aft, gotten along with a SQL information base.
DApps take after web applications, they may have the frontend (GUI when everything is said in done) yet what separates them from Web Apps is the backend. Rather than the Java API and a standard information base, we have a sharp course of action that interfaces with the blockchain and contains the amount of the thinking for the application.
As opposed to standard, joined applications, where the backend code runs on joined masters, DApps have their backend code running on a blockchain network. Each activity needs to meet the plan of the affiliation and is set up on each focal point of the affiliation. Hence, decentralized applications contain the entire pack, from backend to frontend. The sharp agreement is just the backend part of the DApp.
Off-Chain Computation Using Custom Linux Operating System For Reduced Blockchain Load and Faster Processing.Running on a system that functions on both off-chain and Blockchain, CEZO is meant to be a model that compensates for the slow computation and transmission of data via the traditional Blockchain throughput. It does so by providing a two-layer processing solution where simultaneous data processing such as those involving smart contracts are done via Blockchain nodes and nodes via CEZO.
In doing so, the dApp addresses the number perceived drawback of Blockchain services that prevents wider adoption of the technology in most sectors. This will also aid in the creation of new dApp services that are geared specifically towards providing additional computation speeds to both other existing dApps in the market and those that will spring up in the inevitable expansion of the technology’s adoption.
SCALABILITY
As of now, there are significant hurdles with regard to scalability as it pertains to dApps. With the biggest concerns being security and decentralization, many platforms and developers struggle with widespread adoption. This applies to many areas, but most specifically in trading, financial transactions, and gaming. The problem becomes even more prominent during periods of high congestion, thus slowing transfers of data or token access even more.
DAPP DEFINITION
Decentralized applications are open-source platforms that operate autonomously with complete transparency and with no one single individual or special interest controlling the token contracts. Any changes, improvements, or shifts in use are agreed upon by the majority and all relevant data is stored in a decentralized blockchain network that is accessible to the public. Cryptographic tokens are the sole method of access, which are generated via cryptographic algorithms that represent contributing nodes that support the application.
OFF CHAIN COMPUTATION
One of the biggest challenges of blockchain is the issue of slow transaction speeds due to limits of computation power imposed by the multiple nodes that data has to go through. This is the price of security since every line of code is thoroughly checked, even ones that are done in chains that are off the main block.
CALCULATION
Security and privacy are two of the features of blockchain that makes the technology highly sought after. However, it comes at the price of processing speed. Due to the fact that data needs to go through so many nodes before arriving at the final destination, there is an implicit expectation that transaction speeds
LINUX BLOCKCHAIN!
A considerable number of today’s tech tools and applications are built off of the back of the Linux OS. As an open-source platform, it has become the core of many other ecosystems used by giant tech companies such as Google with its Android OS, as just one example. Blockchain is no different, with different services using Linux in different ways.
SMART CONTRACT
Smart contracts have been theorized for decades and was introduced in the mainstream in 1994 by Nick Szabo. However, it was not until the Ethereum blockchain was launched in 2015 that the idea became more widely recognized and used. The idea behind smart contracts is to create programs that would have their own executable codes and would have their own storage of variables that control access in the form of tokens.
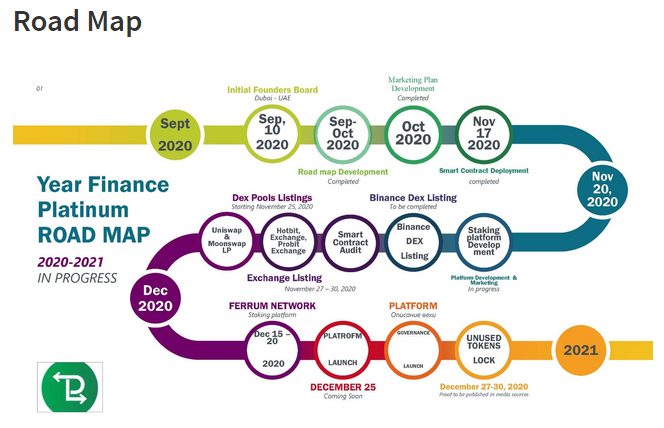
ROADMAP
OUR TEAM